学習させることで、どんどん賢くなっていくLUISをbotサービスで活用するには:認識系API活用入門(終)(2/3 ページ)
コグニティブサービスのAPIを用いて、「現在のコグニティブサービスでどのようなことができるのか」「どのようにして利用できるのか」「どの程度の精度なのか」を検証していく連載。最終回となる今回は、LUIS(Language Understanding Intelligent Service)とMicrosoft Bot Frameworkを組み合わせてbotサービスを作成します。
LUISに接続する処理の作成
実際にプログラムからLUISを呼び出すところを作成します。プログラムの流れとしては非常にシンプルで、下記のようになります。
- ユーザーの入力内容を受け取る
- LUISのAPIにユーザーの入力内容を渡す
- LUISが解析した結果を受け取る
LUISも連載第5回で紹介したComputer Vision APIと同様に、Tokenを使用しない方式です。LUISでは、Tokenを取得せずに直接Endpoint URLにSubscription-Keyを渡すようになっています(ただし、現在LUISはプレビュー扱いであるため、今後どうなるかは分かりません)。
まず、LUISに処理をお願いしてJSON形式で返ってくるデータを受け取るためのクラスを作成します。
メニューバーの「プロジェクト」から「クラスの追加」をクリックします。
追加するのは通常のクラスです。名前を「LUIS.cs」として「追加」ボタンをクリックします。
クラスが追加されたら、下記コードをコピーしてそのクラスにペーストしてください。また、ソースコード73行目のurlは、前回の連載で取得したエンドポイントURLに適宜置き換えてください
ちなみに「LUIS」という名前のフォルダを作成しその下にクラスを置いたので、名前空間が「LUIS_WeatherBotApp.LUIS」となっています。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Net;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Json;
namespace LUIS_WeatherBotApp.LUIS
{
public class LUIS
{
//========================================================
// LUISのデータを受け取るためのクラスたち
//========================================================
public class RootObject
{
public string query { get; set; }
public List<Intents> intents { get; set; }
public List<Entities> entities { get; set; }
}
public class Entities
{
public string entity { get; set; }
public string type { get; set; }
public string startIndex { get; set; }
public string endIndex { get; set; }
public string score { get; set; }
}
public class Intents
{
public string intent { get; set; }
public string score { get; set; }
public List<Actions> actions { get; set; }
}
public class Actions
{
public string triggered { get; set; }
public string name { get; set; }
public List<Parameters> parameters { get; set; }
}
public class Parameters
{
public string name { get; set; }
public string required { get; set; }
public List<Value> value { get; set; }
}
public class Value
{
public string entity { get; set; }
public string type { get; set; }
public string score { get; set; }
}
//========================================================
// LUISの結果が入る
//========================================================
public RootObject LUISResult;
//========================================================
// コンストラクタ
//========================================================
public LUIS(string pMessage)
{
try
{
// LUISにbotで受信したメッセージを投げる
// string url にEndpoint URL を記載
string url = "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/v2.0/apps/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx?subscription-key=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx&staging=true&verbose=true&timezoneOffset=0.0&q=";
url += System.Web.HttpUtility.UrlEncode(pMessage);
var request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
var response = request.GetResponse();
var responseStream = response.GetResponseStream();
if (responseStream == null)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//受け取ったJsonをデシリアライズ
DataContractJsonSerializer dcjs = new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(RootObject));
LUISResult = (RootObject)dcjs.ReadObject(responseStream);
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
天気予報Webサービスに接続する処理の作成
続いて、天気予報を取得する処理です。今回は無料で使用できるLivedoor天気予報のお天気Webサービスを使用します。
APIでは、「city」がパラメーターとして必須になっています。これは都道府県名や県庁所在地が対応しているのですが、名前ではなくIDで渡す必要があります。そのため名前からIDを求める処理が入っています。
LUISと同様に通常のクラスを追加し、名前を「WeatherForecast.cs」とします。
プログラムとしては、こちらのようになります。ちなみに「WeatherForecast」という名前のフォルダを作成しその下にクラスを置いたので、名前空間が「LUIS_WeatherBotApp.WeatherForecast」となっています。
LUISと天気予報を呼び出して応答を返す
続いて、RootDialog.csに、LUISと天気予報を呼び出して応答を返すように変更を加えます。RootDialog.csは以下のようになります。
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Bot.Builder.Dialogs;
using Microsoft.Bot.Connector;
namespace LUIS_WeatherBotApp.Dialogs
{
[Serializable]
public class RootDialog : IDialog<object>
{
public Task StartAsync(IDialogContext context)
{
context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
private async Task MessageReceivedAsync(IDialogContext context, IAwaitable<object> result)
{
try
{
var activity = await result as Activity;
// -----------------------
// LUIS
// -----------------------
string date = "";
string prefecture = "";
LUIS.LUIS luis = new LUIS.LUIS(activity.Text);
if (luis.LUISResult == null)
{
throw new Exception("もう一度お願いしします。");
}
foreach(LUIS.LUIS.Entities entities in luis.LUISResult.entities)
{
switch (entities.type)
{
case "date":
date = entities.entity;
break;
case "prefecture":
prefecture = entities.entity;
break;
}
}
if (date == "" || prefecture == "")
{
throw new Exception("もう一度お願いしします。");
}
// -----------------------
// 天気予報の取得
// -----------------------
WeatherForecast.WeatherForecast weatherForecast = new WeatherForecast.WeatherForecast(prefecture);
if (weatherForecast.weatherResult == null)
{
throw new Exception("その場所の天気予報が取得できませんでした。");
}
WeatherForecast.WeatherForecast.Forecast forecast = null;
switch (date)
{
case "今日":
case "きょう":
forecast = weatherForecast.weatherResult.forecasts[0];
break;
case "明日":
case "あす":
case "あした":
forecast = weatherForecast.weatherResult.forecasts[1];
break;
case "明後日":
case "あさって":
forecast = weatherForecast.weatherResult.forecasts[2];
break;
}
if (forecast == null)
{
throw new Exception("もう一度お願いしします。");
}
string replyMessage = "";
replyMessage += forecast.dateLabel + "は\r\n";
replyMessage += forecast.telop;
if (forecast.temperature.min != null) replyMessage += "\r\n最低気温:" + forecast.temperature.min.celsius + "℃";
if (forecast.temperature.max != null) replyMessage += "\r\n最高気温:" + forecast.temperature.max.celsius + "℃";
await context.PostAsync(replyMessage);
context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync);
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
await context.PostAsync(exception.Message);
context.Wait(MessageReceivedAsync);
}
}
}
}
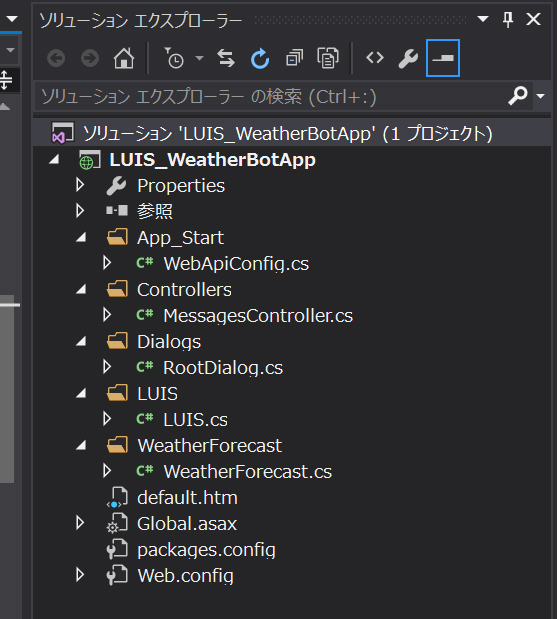
最終的なプロジェクトの構成は、下記のようになります。
Copyright © ITmedia, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
関連記事
 LUIS(自然言語解析サービス)
LUIS(自然言語解析サービス)
LUISはマイクロソフトが提供する自然言語解析サービス。ユーザーが「何をしたいのか」(インテント)とそれに付随する情報(エンティティ)を取り出せる。 LUISを使って頭の悪いLINE Botを作ってみよう!
LUISを使って頭の悪いLINE Botを作ってみよう!
LUIS(自然言語解析サービス)とロケスマWeb(お店発見Webサービス)とGoogle Geocoding APIを使って、ユーザーが探しているお店を教えてくれるLINE Botを作ってみよう! WebhookやHubotを使ってチャットとSubversion、Redmine、Jenkinsを連携させる基本設定とは
WebhookやHubotを使ってチャットとSubversion、Redmine、Jenkinsを連携させる基本設定とは
OSSのチャット基盤であり、Dockerコンテナとして簡単に導入できるRocketChatを使った、コミュニケーション基盤の作り方を学ぶ連載。最終回は、RocketChatと他のアプリケーション(Subversion、Redmine、Jenkins、Zabbix、fluentdなど)と連携させる方法を紹介します。